How to Navigate Divorce Legal Proceedings
Understanding the Fundamentals of Negotiation
Negotiation, at its core, is a process of communication and compromise aimed at reaching a mutually agreeable solution. It involves identifying the needs and interests of all parties involved, actively listening to differing perspectives, and exploring potential options that satisfy those interests. Effective negotiation requires a clear understanding of one's own goals and the ability to adapt strategies based on the evolving dynamics of the conversation. Understanding the underlying principles of negotiation, such as the importance of active listening and the value of building rapport, is crucial for successful outcomes.
A crucial element of negotiation is recognizing and addressing potential power imbalances. Understanding how power dynamics affect the negotiation process is vital for creating a more equitable and productive environment. This awareness allows negotiators to develop strategies that address these imbalances and promote a more balanced exchange of ideas and solutions. Recognizing the potential for miscommunication and proactively working to clarify expectations are also key components of successful negotiation.
Mediation: A Facilitated Approach to Conflict Resolution
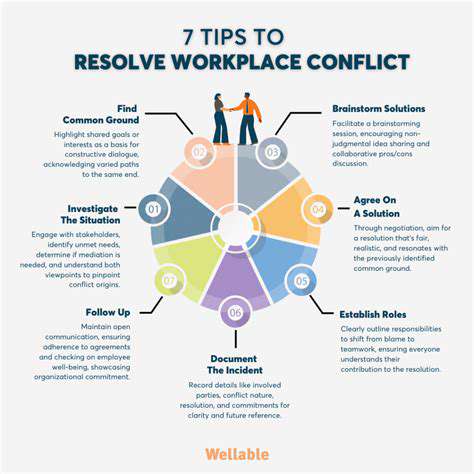
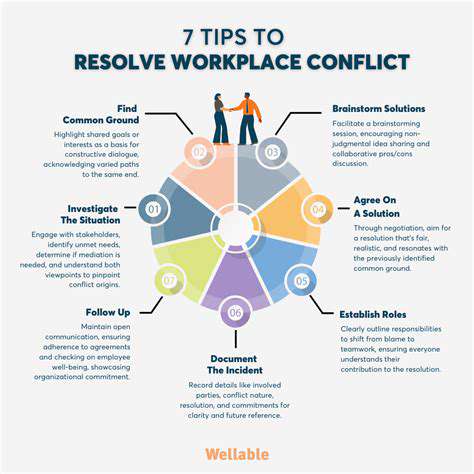
Mediation differs from negotiation in its approach. While negotiation is a direct interaction between parties, mediation involves a neutral third party – the mediator – who facilitates communication and guides the parties towards a resolution. The mediator's role is not to impose a solution but to help the disputing parties identify common ground, explore options, and reach a mutually acceptable agreement. This facilitated process often leads to more creative and sustainable solutions than direct negotiation, especially when emotions run high or communication breakdowns exist.
Mediation is a valuable tool for resolving a wide range of conflicts, from interpersonal disputes to complex commercial disagreements. It promotes a structured and respectful environment for discussions, encouraging open communication and fostering a sense of shared responsibility in the resolution process. This process is significantly beneficial in situations where the parties are unable to effectively communicate or compromise on their own.
The Role of Communication in Dispute Resolution
Effective communication is the cornerstone of both negotiation and mediation. Active listening, clear articulation of needs and interests, and the ability to understand different perspectives are essential for successful outcomes. Understanding non-verbal cues, managing emotions, and maintaining a respectful tone are critical aspects of communication that contribute to a productive and constructive exchange. In situations where parties experience communication breakdowns, the mediator can play a vital role in facilitating productive dialogue and ensuring that all voices are heard.
Choosing the Right Approach: When to Negotiate and When to Mediate
The decision of whether to negotiate or mediate depends on several factors, including the nature of the conflict, the relationship between the parties, and the desired outcome. Negotiation might be the preferred approach when the parties have a strong existing relationship and are capable of direct communication. Mediation, on the other hand, is often more suitable for conflicts involving complex issues, emotional tension, or a breakdown in communication. Careful consideration of the specific circumstances is paramount in determining the most effective approach for resolving a particular dispute.
Ultimately, the choice between negotiation and mediation is often a strategic one. Factors such as the potential for future collaboration, the desired level of control over the outcome, and the time available for the process should all be considered. A skilled professional can often provide guidance in determining the optimal approach based on the unique characteristics of a given situation.
Read more about How to Navigate Divorce Legal Proceedings
Hot Recommendations
- divorce asset division legal checklist
- how to overcome breakup shock step by step
- divorce self growth strategies for single parents
- how to overcome divorce trauma quickly
- emotional recovery tips for breakup survivors
- divorce breakup coping strategies for adults
- how to find effective divorce counseling online
- divorce custody battle resolution strategies
- how to find affordable breakup counseling services
- best co parenting solutions for divorce cases